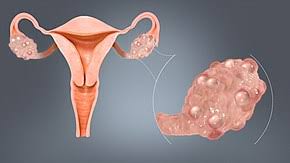
Women have two ovaries that produce eggs and also produce the hormones estrogen and progesterone.
Sometimes, a fluid-filled sac called cyst forms in one of the ovaries. Many women get at least one cyst in their lifetime. In most cases, the cysts are painless and asymptomatic. The cyst becomes a problem when it does not go away or get bigger. It can be painful. There is also the possibility of cancer, but it is rare and its chances increase with age.
Types of ovarian cysts and their causes
There are several types of ovarian cysts, the most common of which are functional cysts. Two types of functional cysts include follicular and corpus luteum cysts.
-
Follicle cyst
-
Jaundice cysts
-
Dermoid cysts
-
Cystadenoma cysts
-
Endometrial cysts
Polycystic ovary
Some women develop a condition called polycystic ovary syndrome. This condition means that the ovaries contain a large number of small cysts. They can cause the ovaries to enlarge. If left untreated, polycystic ovaries can cause infertility.
Symptoms of ovarian cysts
-
Flatulence or swelling
-
Painful bowel movements
-
Pelvic pain before or during the menstrual cycle
-
Pain in the lower back
-
Breast tenderness
-
Nausea and vomiting
Less common symptoms include
-
Ambiguous pain in the lower back and things
-
Problems emptying the bladder or bowel completely
-
Weight gain for no reason
-
Pain during menstruation
-
Abnormal bleeding from the vagina
-
Need to urinate more
Severe symptoms of ovarian cysts that require immediate medical attention include
-
Severe pelvic pain
-
Fever
-
Weakness or dizziness
-
Rapid and continuous breathing
These symptoms can indicate a ruptured cyst or a twisted ovary.
Complications of ovarian cysts
Most ovarian cysts are benign and go away naturally and without treatment. Ovarian torsion is another rare complication of ovarian cysts. A large cyst causes the ovary to twist or move from its original position. In this case, the blood supply to the ovary is cut off, and if left untreated, it can cause damage or death to the ovarian tissue. Ruptured cysts, which are also rare, can cause severe pain and internal bleeding.
Diagnosis of ovarian cysts
Your doctor can diagnose ovarian cysts during a routine pelvic exam. Ultrasound tests can help determine the size, location, shape, and composition (solid or fluid-filled) of a cyst.
Treatment of ovarian cysts
-
Birth control pills
Your doctor may prescribe new ones to prevent ovulation and new cysts.
-
Laparoscopy
If your cyst is small, your doctor can perform a laparoscopy to remove the cyst surgically.
-
Laparotomy
If you have a large cyst, your doctor may surgically remove the cyst through a large incision in your abdomen.
Nutrition and diet therapy in ovarian cysts
-
High-fiber diet: whole grains, fruits, beans, green vegetables, and nuts, almonds, berries, and squash.
-
Omega-3 fatty acids: fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, fish oil, flaxseed, pumpkin seeds, walnuts.
-
Magnesium: helps reduce cramps and pain in ovarian cysts. Broccoli, almonds, nuts, bananas.
-
Alcohol: avoid alcohol as much as possible.
-
Saturated fats: avoid foods that are high in saturated fat.
-
Lean proteins: including fish, tofu and chicken
-
anti-inflammatory foods and spices : including tomatoes, turmeric, kale, olive oil, and almonds.




