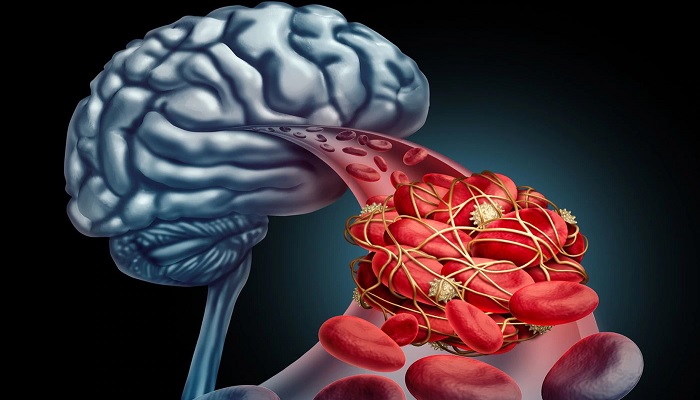
It is estimated that 87% of strokes have ischemic origin and are caused by obstruction.
Hemorrhagic stroke is either intracerebral or subcellular and Occurs when blood from a ruptured artery damages brain tissue. They are cerebral arteries.
Stroke symptoms
Weakness of the face, arms or legs, usually on one side of the body
-
Confusion, difficulty speaking or understanding
Visual disturbances, which may include partial or complete loss of vision.
-
Dizziness or ataxia (stumbling)
Severe headache without known cause
Nutritional considerations in stroke
-
Healthy eating pattern
Healthy eating patterns have a relative absence of foods that are high in energy, High saturated fats (e.g. high fat meats and dairy products) and fried foods, Processed and that are defined by high glycemic index.
Existence of fruits, vegetables, soy and Other legumes, nuts, unsaturated fats, and low-energy foods and high fiber is another characteristic of healthy eating patterns.
-
Consumption of fish
Consumption of fish and consumption of omega-3 fatty acids with preventive properties to reduce the risk of infection. They have a relationship with cerebrovascular disease and reduce the risk compared to consuming less.
Ischemic stroke in men and women and the risk of stroke in general.
-
Diets rich in fruits, vegetables and fiber and low in carbohydrates (refined)
Eating more fruits and vegetables is associated with a lower risk of stroke.
There is a dose-response relation between these, Consumption of every 200 grams of fruit (about two small apples a day) reduces the risk of stroke by 32% and consumption of every 200 grams of vegetables reduces the risk of stroke by 11%.
Although most recent studies show that eating citrus kernels, apples, pears and vegetable leaves protects against stroke.
Other studies show that the level of lycopene in the blood (a carotenoid found almost exclusively in tomato products reduces the risk of stroke by about 20%. In addition to carotenoids such as lycopene, dietary fiber, vitamin C, these foods, Vitamin E provides folate and flavonoids.
All of this has been associated with a reduced risk of stroke in epidemiological studies.
-
Eat less sodium.
Consuming more sodium (compared to small amounts) increases the risk of stroke by about 25%. Potassium intake, on the other hand, is associated with a lower risk of stroke.
- Have a healthy weight
Being overweight increases the risk of stroke. The risk of stroke is 22% higher in overweight people and 64% higher in obese people.
Adequate levels of vitamin D.
Compared to people with the highest levels of vitamin D in the blood, people with the lowest levels of vitamin D are 64% more likely to have a stroke.
- Choose the right drink
Consuming three cups of tea a day reduces the risk of stroke by almost 20%. When comparing people who drink coffee with people who do not drink coffee reduces the risk of stroke in the first group by 13%
It is also recommended to limit alcohol consumption.




