Stomach bypass
Stomach bypass or obesity surgery is a method that aims to help manage obesity. Obesity can increase the risk of diabetes, osteoarthritis, high blood pressure, heart disease, and other health conditions. Health experts recommend losing weight to promote overall health. Stomach bypass is one of the ways to treat obesity and help to lose weight.
Definition of gastric bypass
If changes in lifestyle would be ineffective, your doctor might recommend surgery. In general, gastric bypass can help you lose weight in one of three ways:
Limiter: The surgeon reduces the size of the stomach.
Malabsorption: The surgeon decreases the amount of small intestine that food can pass through.
Mixtures: These methods limit food intake and cause malabsorption.
Reasons for gastric bypass
• Disease returning acid to the esophagus
• Heart disease
• High blood pressure
• High cholesterol
• Obstructive sleep apnea
• Type 2 diabetes
• Stroke
• Sterility
Uses of gastric bypass
Your body mass index (BMI) is 40 or higher (severe obesity).
If your body mass index is 35 to 39.9 (obesity), you may face a serious weight problem such as; type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, or sleep apnea. Weight loss surgery is urgent when the index is 30 to 34, in line with the fatness problem in some cases.
Adjustable laparoscopic gastric bandage
Laparoscopic adjustable gastric bandage (LAGB) is one of the least invasive weight-limiting surgeries. People sometimes refer to it as a gastric sleeve.
Vertical sleeve gastrectomy
Vertical sleeve gastrectomy (VSG) is a procedure commonly known as "gastric puncture."
By surgery, a surgeon permanently removes some part of the stomach and limits the amount of food a person can consume.
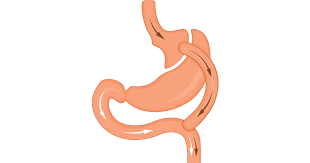
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass
The surgeon reduces the size of the stomach to about the size of a golf ball. This method acts as malabsorption because the food absorption through it is less than normal duration time digestion.
Recovery time and type of diet in gastric bypass
Recovery time depends on the type of gastric bypass procedure. In general, the more invasive it is, the longer it takes to heal.
The length of time a person can recover can also depend on the complications during surgery.
To ensure no side effects, dietary changes after gastric bypass are necessary and should include the following steps:
• Refined liquids
•liquids
• Soft food
• Regular meals
After gastric bypass surgery
Your doctor will advise you to take vitamin and mineral supplements after gastric bypass surgery, including a multivitamin with iron, calcium, and vitamin B12.
You may experience changes in the first three to six months after gastric bypass surgery, including:
• The body is in pain
• Feeling tired, as if you have the flu
•Feeling cold
•dry skin
• Low back and hair loss
• Mood swings
Risks and complications of gastric bypass surgery
• Excessive bleeding
• Infection
• Adverse reactions to anesthesia
• Blood clotting
• Pulmonary or respiratory problems
• Leaks in your digestive tract
Long-term risks and complications of gastric bypass can include the following:
• Ileus
• Dumping syndrome, diarrhea, nausea, or vomiting
• Gallstones
• Hernia
• Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)
• Malnutrition
• Perforation of the stomach
• Wounds
• Vomit
• Rarely, the side effects of gastric bypass can be fatal.
Other complications of gastric bypass
• Dumping syndrome
• Leakage
• Constipation
• Skin folds
• Vitamin deficiency
• Do not lose weight




