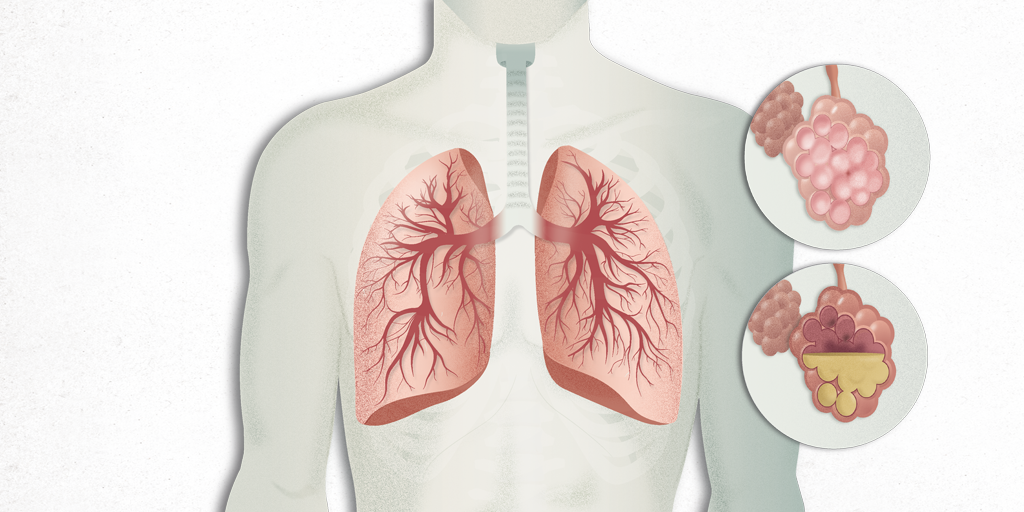
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs that affects the air sacs. Sometimes it fills them with liquids or pus. Pneumonia can be caused by a number of various organisms, including bacteria, viruses and fungi as well Aspiration (inhalation) of a foreign object. Pneumonia affects millions of people every year; especially children under 5 years and adults over 65 years as well as people who are hospitalized or have chronic illnesses or suppress the immune system.
Common causes of pneumonia
-
bacterias
Bacterial pneumonia is the most common type of pneumonia, usually treated with antibiotics. -
viruses
It is the most common cause of pneumonia in children under 5 years old. Most people with viral pneumonia recover within one to three weeks without treatment. -
Mushrooms
Fungal pneumonia usually occurs in people whose immune systems are compromised or who have chronic health problems. -
Aspiration
Aspiration pneumonia or accumulation of infectious substances in the lungs due to the presence of a foreign body can make it difficult to breathe. This problem is more common in the elderly, who may have difficulty swallowing. The risk of aspiration pneumonia is also high during anesthesia, which is why patients are asked not to eat before surgery.
Lifestyle risk factors for pneumonia
-
smoking
-
Drugs or alcohol abuse
-
Malnutrition
-
Poor dental health
Symptoms of pneumonia
-
Fever, sweating or chills
-
Cough (often severe) that causes sputum.
-
Shortness of breath
-
Chest pain when coughing or taking deep breath
-
Feeling weak and tired
-
Changes in mental status in people at 65 and older
-
Loss of appetite
-
Nausea, diarrhea or vomiting
Nutrition in pneumonia
-
Whole grains
The carbohydrate content of whole grains such as quinoa, brown rice and oats provides the body with the necessary energy. The B vitamins and selenium in them help produce energy and control body temperature and strengthen the immune system, respectively. -
Water
Drinking plenty of fluids is highly recommended. Not only water but also other liquids such as juices help to lubricate the mucous membranes in the lungs and eliminate harmful toxins and foreign particles that cause obstruction in the respiratory tract. -
Protein rich foods
Foods such as nuts, seeds, beans, white meat and cold-water fish such as salmon and sardines have anti-inflammatory properties and also help repair damaged tissues and create new tissues in the body. -
Green leafy vegetables
Leafy vegetables such as cabbage, lettuce and spinach are rich in nutrients and contain antioxidants that protect the body against infectious agents. -
Fruits
Citrus fruits that are rich in vitamin C, such as oranges, as well as berries and kiwis, help strengthen the immune system and thus accelerate recovery. Fruits also contain antioxidants that protect the body against external factors. -
probiotic
Foods such as yogurt contain probiotics that inhibit the growth of pneumonia-causing pathogens and also boost the body's immune system by increasing the amount of good bacteria in the gut. -
Honey
Honey is effective in treating coughs and colds (symptoms of pneumonia) and has antibacterial and antimicrobial properties. -
Fenugreek tea
Fenugreek tea may help treat the persistent cough experienced in pneumonia. Fenugreek seeds can also help a person sweat, which lowers body temperature during a fever. -
Turmeric
Acts as a mucolytic; This means that it helps to break down and lubricate the mucosa and prevent damage to the bronchial tubes, which leads to easy breathing. Even turmeric has anti-inflammatory properties that reduce chest pain. This food can be consumed with both milk and tea. -
Ginger
Ginger has anti-inflammatory and anti-bacterial properties and helps reduce chest pain.




