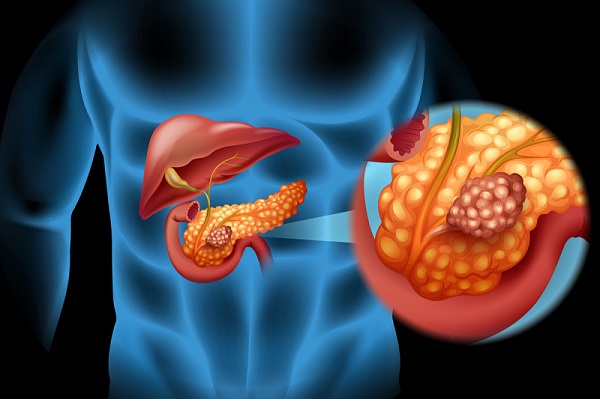
Pancreatic cancer
What is pancreatic cancer?
Pancreatic cancer occurs in the tissues of the pancreas, which is a vital organ of the endocrine glands located behind the stomach. The pancreas produces digestive hormones to break down fats, carbohydrates, and proteins.
Symptoms of pancreatic cancer
Some common symptoms can be subtle. They are:
• Loss of appetite
• Unwanted weight loss
•Abdominal (stomach) or back pain
•blood clotting
•Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
• Depression
Causes of Pancreatic Cancer
The cause of pancreatic cancer is unknown. This type of cancer occurs when abnormal cells inside the pancreas begin to grow and form a tumor.
Stages of pancreatic cancer
Stage1: Tumors are present only in the pancreas.
Stage2: Tumors have spread to nearby abdominal tissues or lymph nodes.
Stage3: Cancer has spread to the main arteries and lymph nodes.
Stage4: Tumors have spread to other organs, such as the liver.
Stage 4 Pancreatic cancer
Stage 4 Pancreatic cancer has spread beyond the original site to distant sites such as, the brain, or the bones.
signs:
Pain in the upper abdomen
• Back pain
• Fatigue
• Jaundice
• Loss of appetite
•Weight Loss
•Depression
Treatment methods:
Chemotherapy
Pain relief treatments
Bile duct bypass surgery
Bile duct stent
Gastric bypass surgery
The five-year survival rate for stage 4 pancreatic cancer is 3%.
Stage 3 pancreatic cancer
Stage 3 is a tumor in the pancreas and possibly nearby areas, such as lymph nodes or blood vessels. Pancreatic cancer has not spread to distant places at this stage.
Signs:
• Back pain
• Pain or tenderness in the upper abdomen
• Loss of appetite
•Weight Loss
• Fatigue
• Depression
Treatments:
• Surgery to remove part of the pancreas (Whipple method)
• Anti-cancer drugs
•Radiotherapy
The five-year survival rate for stage 3 pancreatic cancer is 3 to 12 percent.
Stage 2 pancreatic cancer
Stage 2 pancreatic cancer remains in the pancreas and may spread to several nearby lymph nodes. It has not laid to nearby tissues or blood vessels out and has not broadened to other parts of the body.
It is hard to diagnose pancreatic cancer in the early stages, including stage 2.
Signs:
• Jaundice
• Change in urine color
• Pain or tenderness in the upper abdomen
•Weight Loss
• Loss of appetite
• Fatigue
Treatment:
•surgery
• Radiation
•Chemotherapy
• Targeted drug treatments
• Treatment of pancreatic cancer
•surgery
All or some parts of the pancreas must be surgically removed.
Radiotherapy
Radiation therapy uses X-rays and other high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
Chemotherapy
In some cases, your doctor may combine other treatments with chemotherapy.
Targeted treatment
This type of cancer treatment uses drugs or other measures to kill specific target cancer cells.
Diagnosis of pancreatic cancer
A CT or MRI scan helps to get a complete and accurate picture of your pancreas.
• Endoscopic ultrasound
• Biopsy or tissue sample of the pancreas
• blood test
Is pancreatic cancer treatable?
Pancreatic cancer is treatable. Two types of surgery, Whipple surgery or pancreatectomy, can remove part or all of the pancreas. It kills the primary cancerous tumor.
Risk factors for pancreatic cancer
Smoking: 30% of cancers are related to smoking.
• Obesity
• Do not exercise regularly
•Consume high-fat diets
• Drink large amounts of alcohol
• Diabetes
• Working with pesticides and chemicals
• Chronic inflammation of the pancreas
• Liver damage
•Being African or American




