Gout
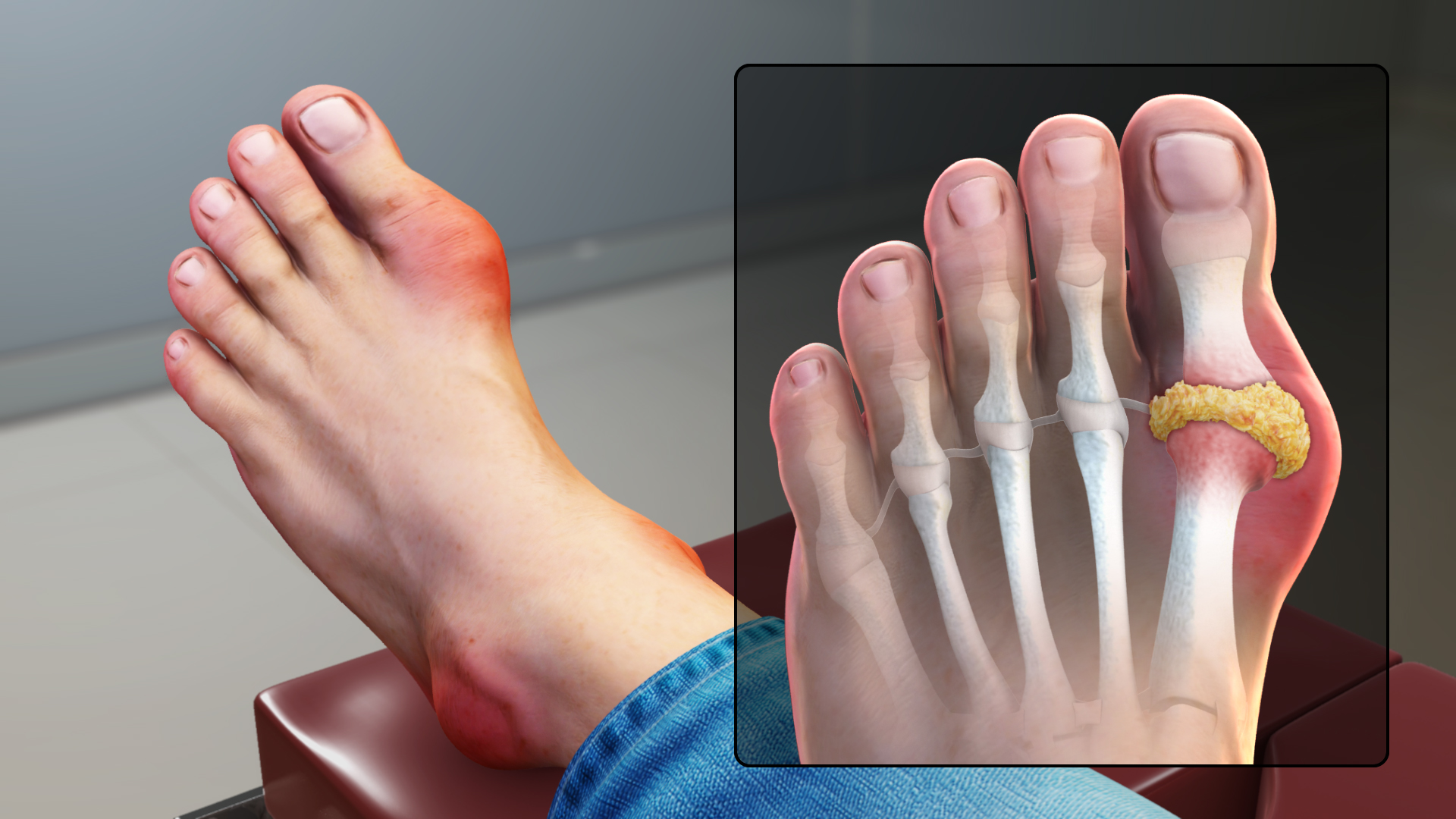
Gout is a common and complex type of osteoarthritis that can affect anyone. This feature is characterized by sudden and severe pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness in the joints, often at the extensive toe base.
A gout attack can happen suddenly and often wakes you up in the middle of the night with the feeling that the big toe is burning. The damaged joint is hot, swollen, and so sensitive that even the sheet's weight on it seems unbearable.
Signs
Signs and symptoms of gout almost always occur suddenly and often at night
•Intense joint pain Gout usually affects the big toe joint but can occur in any joint. Other joints that are commonly involved include the ankle, knee, elbow, wrist, and toes. The pain is probably severe in the first four to 12 hours after it begins.
•Lingering discomfort After the most severe pain has subsided, some joint discomfort may last from a few days to a few weeks. Subsequent attacks are likely to be longer and affect more joints.
•Inflammation and redness of the affected joint or joints become swollen, tender, hot, and red.
•Limited range of motion. As gout progresses, you may not be able to move the joints normally.
When to see a doctor
If experiencing sudden, intense pain in a joint, call the doctor. Gout that goes untreated can lead to worsening pain and joint damage.
Seek medical care immediately if having a fever and a joint is hot and inflamed, which can be a sign of infection.
Causes
Gout occurs when urate crystals accumulate in the joints, causing inflammation and severe pain from a gout attack. When having large amounts of uric acid in the blood, urine crystals can form. When the body breaks down purine - it produces uric acid - substances found naturally in the body. Purine is also found in certain foods such as steak, organ meats, and seafood. Other foods also boost higher uric acid levels, such as alcoholic beverages, especially beer, and sugary fruit drinks (fructose).
Prevention
Drink plenty of fluids. Stay well-hydrated, including plenty of water. Limit how many sweetened beverages are drinking, especially those sweetened with high-fructose corn syrup.
Limit or avoid alcohol. Talk with the doctor about whether any amount or type of alcohol is safe. Recent evidence suggests that beer may be particularly likely to increase the risk of gout symptoms, especially in men.
Get the protein from low-fat dairy products. Low-fat dairy products may have a protective effect against gout, so these are the best-bet protein sources.
Limit the intake of meat, fish, and poultry. A small amount may be tolerable, but pay close attention to what types — and how much — seem to cause problems.
Maintain desirable body weight. Choose portions that allow you to maintain a healthy weight. Losing weight may decrease uric acid levels in the body. However, avoid fasting or rapid weight loss since doing so may temporarily raise uric acid levels.




