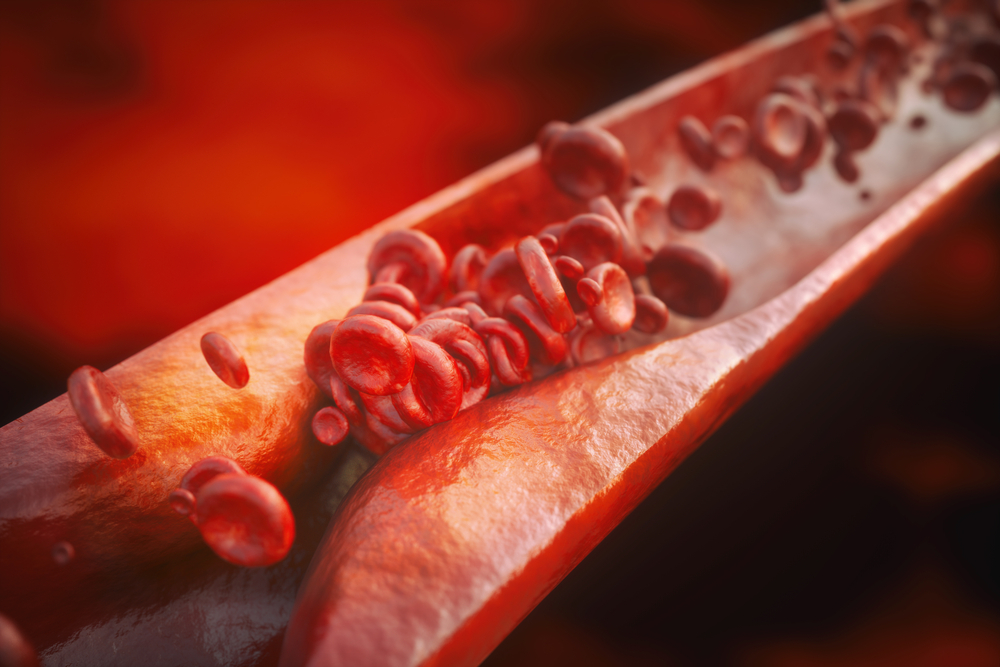
Atherosclerosis is a very common type of atherosclerosis, in which deposits called plaque to form on the walls of the arteries that carry blood that contains oxygen and other nutrients from the heart to other parts of the body. Atherosclerosis can cause kidney damage, reduced blood flow to the brain and organs, and coronary heart disease. Atherosclerosis is a major cause of stroke and heart attack. It can start in your thirties and early twenties. It is more common in men up to the age of 45. But And after menopause, its prevalence increases in women.
Symptoms are common
You usually would not have atherosclerosis symptoms until an artery is would be so narrowed or clogged that it cannot supply adequate blood to your organs and tissues. Sometimes a blood clot completely blocks blood flow, or even breaks apart and can trigger a heart attack or stroke.
Unless atherosclerosis has reached an advanced stage, it is often asymptomatic. The onset of symptoms depends on which part of the body's blood supply is reduced, and how severe and widespread the disease is.
Muscle cramps, when the arteries of the foot are involved. (The foot arteries spasm can cause muscle cramps.)
Angina pectoris or heart attack, when the arteries of the heart are involved. (Angina pectoris or heart attack can be related to coronary artery disease).
Stroke, or a sudden and temporary reduction in blood flow to the brain but without stroke, if the arteries leading to the neck and then to the brain are involved.
reasons
Fatty tissue fragments, which contain low-density lipoprotein (the same as bad cholesterol) and damage the artery wall, often build up at the junction of the arteries. The formation of these sediments may begin even in early youth. The lining of the inner wall lining of the artery traps the fatty substances in the blood at these junctions and branches. With the accumulation of fatty substances, the flexibility of the artery decreases, and its internal space becomes narrower. As a result, blood flow is impaired. On the other hand, these deposits may rupture or rupture and form a blood clot on them, which clogs the vein.
High blood pressure, high cholesterol (high concentration of low-density lipoprotein )(bad cholesterol) and low concentration of high-density lipoprotein (good cholesterol), age over 60, male gender, stress, diabetes mellitus, dementia, dementia Malnutrition (eating too much fat and cholesterol) and a family history of atherosclerosis are aggravating factors.
Diet
Eat healthy foods. A heart-healthy diet based on fruits, vegetables, and whole grains — and low in refined carbohydrates, sugars, saturated fat, and sodium — can help you control your weight, blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar. substituting whole-grain bread in place of white bread; grabbing an apple, a banana, or carrot sticks as a snack; and reading nutrition labels as a guide to controlling the amount of salt and you eat. Use monounsaturated fats, such as olive oil, and reduce or eliminate sugar and sugar substitutes.
It's thought that some foods and herbal supplements can help reduce your high cholesterol level and high blood pressure, two major risk factors for developing atherosclerosis. With your doctor's OK (with your Doctor's prescription), you might consider these supplements and products:
-
Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA)
-
Barley
-
Beta-sitosterol (found in oral supplements and some, such as Promise Activ)
-
Black tea
-
Blond psyllium (found in seed husk and products such as Metamucil)
-
Calcium
-
Cocoa
-
Cod liver oil
-
Coenzyme Q10
-
Fish oil
-
Folic acid
-
Garlic
-
Green tea
-
Oat bran (found in oatmeal and whole oats)
-
Sitostanol (found in oral supplements and some, such as Benecol)
-
Vitamin C
Stop smoking. Smoking damages your arteries. If you smoke or use tobacco in any form, quitting is the best way to halt the progression of atherosclerosis and reduce your risk for complications.
Exercise most days of the week. Regular exercise can condition your muscles to use oxygen more efficiently. Physical activity can also improve circulation and promote the development of new blood vessels that form a natural bypass around obstructions (collateral vessels). Exercise helps lower blood pressure and reduces your risk of diabetes.




